How does my internet get to my house?
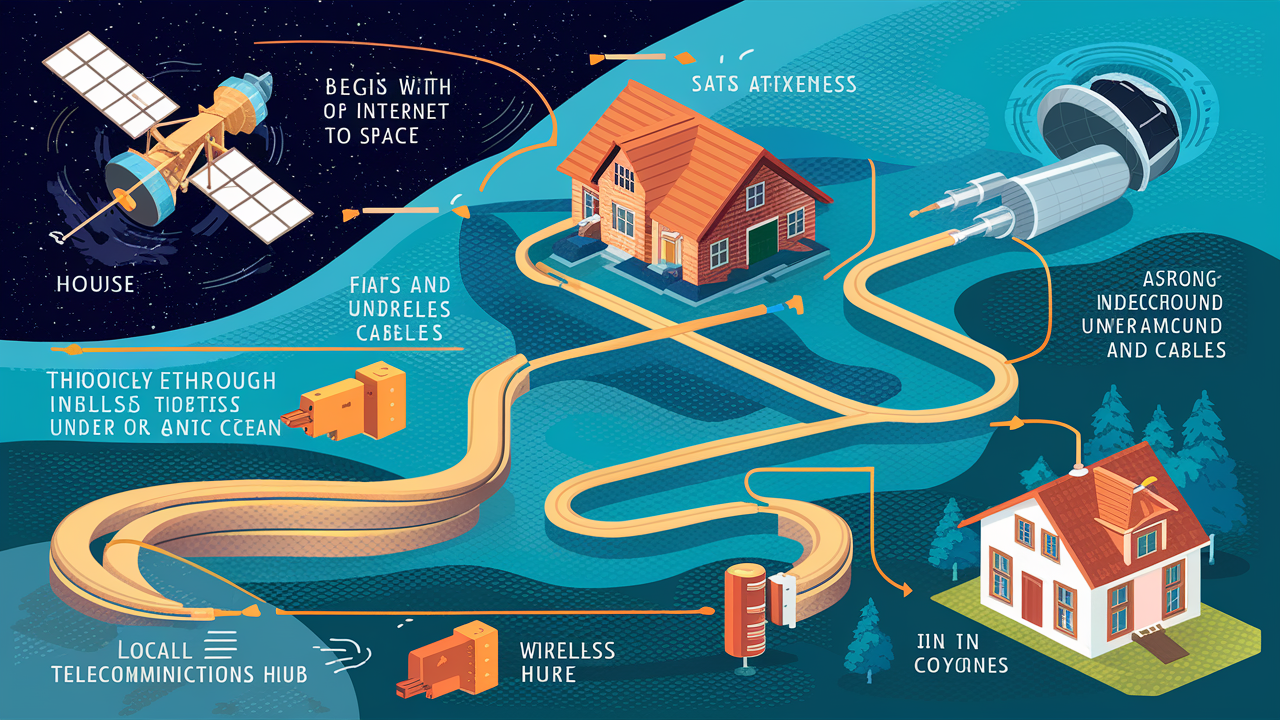
Do you ever think about how you get internet service in your house and how it becomes so convenient that you can use it all day for browsing, watching movies, and sending messages? You get to connect your house to the internet through a well-coordinated network of cables, wires, satellites, towers, servers, etc. So let us dissect it further to understand the process followed by the strategy.
The Internet Backbone
The first is the actual internet which is a huge network of fibre-optic cables and conduits all across the globe for transmitting large volumes of data. Some of the major telecommunication companies own the backbone that is made up of cables laid underground and under the oceans. The backbone links regional networks across countries and continents.
Ensuring that the Signal is received in your region
From the backbone, internet access extends closer to your location through the regional Internet networks and ISPs. ISPs can connect to the backbone or regional network through IXPs and then transfer the data to the local networks.
This means that your ISP has servers and other infrastructure that is used for receiving signals from regional networks and transmitting them to the local community. They may have fiber optic cables, telephone lines, coaxial cables, satellite networks, and cellular towers for wireless internet. These transport the signal closer to your neighborhood.
The Last Mile
The “last mile” is the physical connections that take physical infrastructure right into your house and into the ISP servers. This usually entails placing cables all around a neighborhood to connect houses. Options include:
- Fiber optic cables for the highest connection speed
- Telephone lines that are deployed to operate through DSL connections
- Coaxial cables with cable Internet. Still, it is worth highlighting that coaxial cables can be used not only for transmitting video signals but also for providing an Internet connection through cable Internet.
- Satellite dishes capture signals from orbiting satellites
- Towers that are static and emit wireless fidelity signals.
In the case of fiber optic internet, the ISP gets as close to your house as possible, and sometimes to the door. Technicians install a fiber optic box at your house, with the cable running inside to the router/modem.
Regarding other connection types, such as cable or DSL, the ISP lays the cable to a junction box within the neighborhood. They install a smaller cable than the one used to connect the junction to your home.
Getting Inside Your House
Once the outdoor cables are to your house, they plug into networking devices within the house such as a modem and router to turn the signal to WiFi and wired ports.
If you want internet access through coaxial cables, the cable line connects directly to a cable modem that demodulates the signals and outputs Ethernet ports and Wi-Fi.
For fiber optic or DSL via telephone lines, the cables first plug into special modems which translate light pulses or telephone signals into something that computers are capable of recognizing. The modem connects directly to your WiFi router that sends the wireless signal to every corner of your home allowing all devices to join the network.
Managing the Traffic
Now that millions of people go online every day, ISPs and backbone networks employ sophisticated traffic routing systems to avoid such problems. Other facilities include servers found in data centers that assist in the management of the flow of traffic.
While using the internet, individual packets of data relay requests and pass on information between your devices, the servers you connect to, or your ISP. To reach your Facebook feeds, YouTube videos, and web pages, requests have to travel through junctions and cables along the best routes. This is because traffic control systems enable cars to maintain high speeds.
That, in its simplest form does tells the story of how your digital requests travel from a global Internet network down the wires into your house whenever you log on. Making Internet connectivity easily accessible requires a huge, complex system working in the background. The next time your WiFi is slow, imagine the complex technological system that is needed for all these massive amounts of data to be delivered immediately to your household full of devices.
Upgrade to faster, more reliable AT&T Fiber Internet today! Call us at +1 844-905-5002 and get connected with speeds that keep you ahead.





